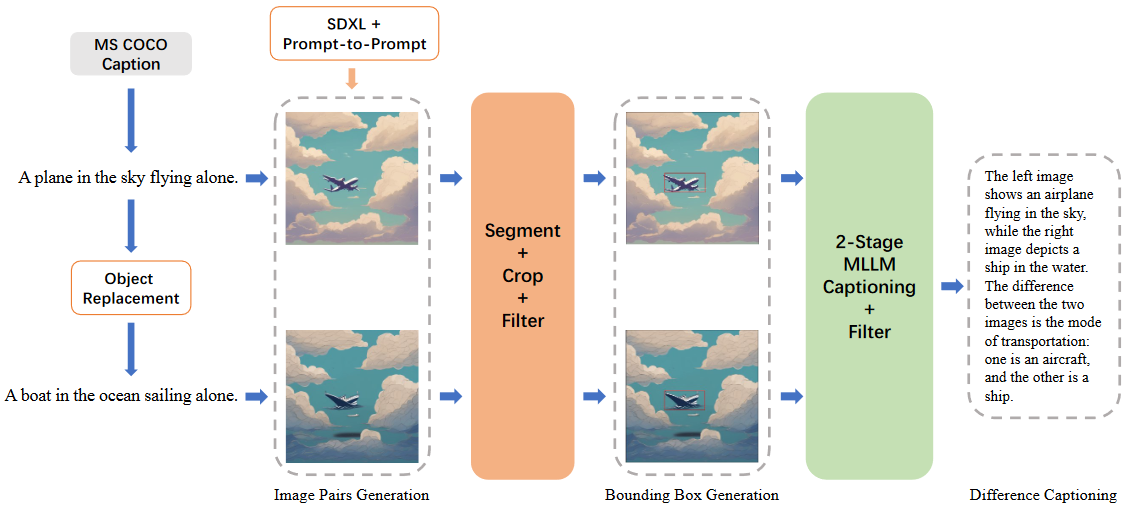
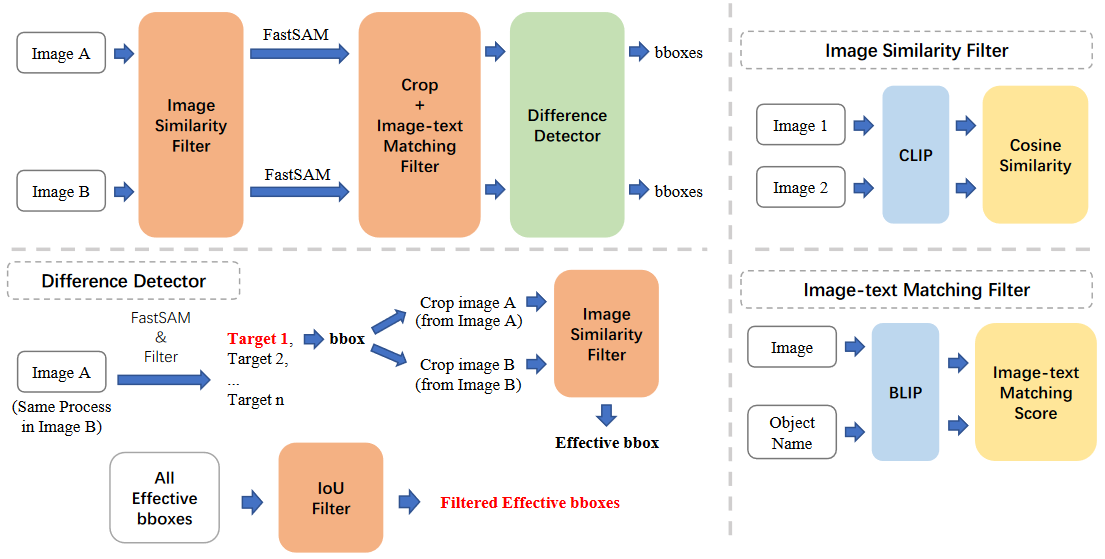
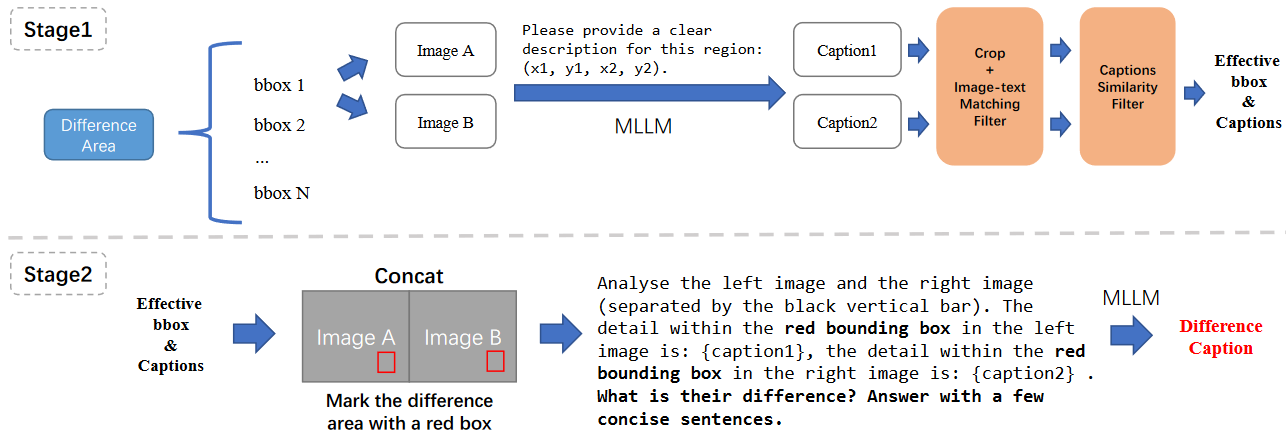
两个顶点的最短路径
leetcode433 最小基因变化
基因序列可以表示为一条由 8 个字符组成的字符串,其中每个字符都是
'A'、'C'、'G' 和 'T' 之一。 假设我们需要调查从基因序列 start 变为 end
所发生的基因变化。一次基因变化就意味着这个基因序列中的一个字符发生了变化。
例如,"AACCGGTT" --> "AACCGGTA" 就是一次基因变化。 另有一个基因库
bank
记录了所有有效的基因变化,只有基因库中的基因才是有效的基因序列。(变化后的基因必须位于基因库
bank 中) 给你两个基因序列 start 和 end ,以及一个基因库 bank
,请你找出并返回能够使 start 变化为 end
所需的最少变化次数。如果无法完成此基因变化,返回 -1 。
注意:起始基因序列 start
默认是有效的,但是它并不一定会出现在基因库中。
题解
BFS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 int minMutation (string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank) if (bank.size () == 0 ) return -1 ; int total_diff = 0 ; vector<bool > visit (bank.size(), false ) ; queue<string> genes; genes.push (startGene); while (genes.size ()) { total_diff ++; for (int n = genes.size (); n > 0 ; n --) { string gene = genes.front (); genes.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < bank.size (); i ++) { if (visit[i]) continue ; int count_diff = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < gene.size (); j ++) { if (gene[j] != bank[i][j]) count_diff ++; } if (count_diff == 1 ) { if (bank[i] == endGene) return total_diff; genes.push (bank[i]); visit[i] = true ; } } } } return -1 ; }
leetcodeLCP35 电动车游城市
小明的电动车电量充满时可行驶距离为 cnt,每行驶 1 单位距离消耗 1
单位电量,且花费 1 单位时间。小明想选择电动车作为代步工具。地图上共有 N
个景点,景点编号为 0 ~ N-1。他将地图信息以 [城市 A 编号,城市 B
编号,两城市间距离] 格式整理在在二维数组 paths,表示城市 A、B
间存在双向通路。初始状态,电动车电量为
0。每个城市都设有充电桩,charge[i] 表示第 i 个城市每充 1
单位电量需要花费的单位时间。请返回小明最少需要花费多少单位时间从起点城市
start 抵达终点城市 end。
思路
通过 Dijkstra 方法,更新起点到各个顶点的最短花费单位时间 代码参考
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 int electricCarPlan (vector<vector<int >>& paths, int cnt, int start, int end, vector<int >& charge) int n = charge.size (); vector<vector<pair<int , int >>> edges (n); for (auto p : paths) { edges[p[0 ]].emplace_back (p[1 ], p[2 ]); edges[p[1 ]].emplace_back (p[0 ], p[2 ]); } vector<vector<int >> cost (n, vector <int >(cnt + 1 , INT_MAX)); cost[start][0 ] = 0 ; priority_queue<tuple<int , int , int >, vector<tuple<int , int , int >>, greater<>> q; q.emplace (0 , start, 0 ); while (q.size ()) { auto [cost1, n1, o1] = q.top (); q.pop (); if (cost1 > cost[n1][o1]) continue ; if (n1 == end) return cost1; if (o1 < cnt) { int new_cost = cost1 + charge[n1]; if (new_cost < cost[n1][o1 + 1 ]) { cost[n1][o1 + 1 ] = new_cost; q.emplace (new_cost, n1, o1 + 1 ); } } for (auto [n2, cost2] : edges[n1]) { if (o1 < cost2) continue ; int new_cost = cost1 + cost2; int new_o = o1 - cost2; if (new_cost < cost[n2][new_o]) { cost[n2][new_o] = new_cost; q.emplace (new_cost, n2, new_o); } } } return -1 ; }
leetcode909 蛇梯棋
给你一个大小为 n x n 的整数矩阵 board ,方格按从 1 到 n2
编号,编号遵循 转行交替方式 ,从左下角开始 (即,从 board[n - 1][0]
开始)每一行交替方向。
玩家从棋盘上的方格 1 (总是在最后一行、第一列)开始出发。
每一回合,玩家需要从当前方格 curr 开始出发,按下述要求前进:
选定目标方格 next ,目标方格的编号符合范围 [curr + 1, min(curr + 6,
n2)] 。 该选择模拟了掷 六面体骰子
的情景,无论棋盘大小如何,玩家最多只能有 6 个目的地。
传送玩家:如果目标方格 next
处存在蛇或梯子,那么玩家会传送到蛇或梯子的目的地。否则,玩家传送到目标方格
next 。 当玩家到达编号 n2 的方格时,游戏结束。 r 行 c
列的棋盘,按前述方法编号,棋盘格中可能存在 “蛇” 或 “梯子”;如果
board[r][c] != -1,那个蛇或梯子的目的地将会是 board[r][c]。编号为 1 和
n2 的方格上没有蛇或梯子。
注意,玩家在每回合的前进过程中最多只能爬过蛇或梯子一次:就算目的地是另一条蛇或梯子的起点,玩家也
不能 继续移动。
举个例子,假设棋盘是 [[-1,4],[-1,3]] ,第一次移动,玩家的目标方格是 2
。那么这个玩家将会顺着梯子到达方格 3 ,但 不能 顺着方格 3
上的梯子前往方格 4 。 返回达到编号为 n2
的方格所需的最少移动次数,如果不可能,则返回 -1。
思路
将棋盘的各个格子看作图顶点,顶点之间的移动步数作为边长,可将问题转换为最短路径问题。
在使用 Dijkstra 算法时可能会遇到一些细节问题:
在建立连接路径时
建立 6 步跳跃关系时,可以通过编号循环累加
建立梯子和蛇的关系时,可以利用编号与坐标的对应关系,通过二维数组判断当前是否可以跳跃
不能连续跳跃,且必须跳跃
在判断下一个节点时,处理跳跃关系(具体在代码中体现),这样就避免了连跳的可能性
可以不使用优先队列
由于每次遍历时,每条路径的增长均为 1,所以不存在更短的路径
leetcode 公交路线
给你一个数组 routes ,表示一系列公交线路,其中每个 routes[i]
表示一条公交线路,第 i 辆公交车将会在上面循环行驶。
例如,路线 routes[0] = [1, 5, 7] 表示第 0 辆公交车会一直按序列 1
-> 5 -> 7 -> 1 -> 5 -> 7 -> 1 -> ...
这样的车站路线行驶。 现在从 source
车站出发(初始时不在公交车上),要前往 target 车站。
期间仅可乘坐公交车。
求出 最少乘坐的公交车数量 。如果不可能到达终点车站,返回 -1 。
抽象路线为图节点
因为只需要统计路线数,所以不需要考虑经过节点数量
因此,可以将路线作为节点,有重合站点的路线建立边,再统计起始线路到达目标线路的经过路线数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 int numBusesToDestination (vector<vector<int >>& routes, int source, int target) if (source == target) return 0 ; int n = routes.size (); unordered_map<int , set<int >> stationRoute; queue<int > iterRoutes; vector<int > dis (n, 10e7 ) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { auto route = routes[i]; bool find = false ; for (auto station : route) { stationRoute[station].insert (i); if (station == source) { find = true ; } } if (find) { iterRoutes.emplace (i); dis[i] = 1 ; } } vector<int > visited (n, false ) ; while (iterRoutes.size ()) { int curRoute = iterRoutes.front (); iterRoutes.pop (); if (visited[curRoute]) continue ; visited[curRoute] = true ; for (auto station : routes[curRoute]) { if (station == target) return dis[curRoute]; for (auto route : stationRoute[station]) { if (visited[route]) continue ; if (dis[curRoute] + 1 < dis[route]) { dis[route] = dis[curRoute] + 1 ; iterRoutes.emplace (route); } } } } return -1 ; }
判断图中节点可达
leetcode399 除法求值
给你一个变量对数组 equations 和一个实数值数组 values
作为已知条件,其中 equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] 和 values[i] 共同表示等式 Ai
/ Bi = values[i] 。每个 Ai 或 Bi 是一个表示单个变量的字符串。
另有一些以数组 queries 表示的问题,其中 queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] 表示第 j
个问题,请你根据已知条件找出 Cj / Dj = ? 的结果作为答案。 返回
所有问题的答案 。如果存在某个无法确定的答案,则用 -1.0
替代这个答案。如果问题中出现了给定的已知条件中没有出现的字符串,也需要用
-1.0 替代这个答案。
注意:输入总是有效的。你可以假设除法运算中不会出现除数为 0
的情况,且不存在任何矛盾的结果。
注意:未在等式列表中出现的变量是未定义的,因此无法确定它们的答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 vector<double > calcEquation (vector<vector<string>>& equations, vector<double >& values, vector<vector<string>>& queries) { vector<double > result; map<string, int > nodes; for (auto eq : equations) { string a = eq[0 ], b = eq[1 ]; if (! nodes.count (a)) { nodes[a] = nodes.size (); } if (! nodes.count (b)) { nodes[b] = nodes.size (); } } int nodeNum = nodes.size (); vector<vector<double >> connect (nodeNum, vector <double >(nodeNum, -1.0 )); for (int i = 0 ; i < nodeNum; i ++) { connect[i][i] = 1.0 ; } for (int i = 0 , len = equations.size (); i < len; i ++) { auto eq = equations[i]; double val = values[i]; string a = eq[0 ], b = eq[1 ]; int ia = nodes[a], ib = nodes[b]; connect[ia][ib] = val; connect[ib][ia] = 1.0 / val; } for (int k = 0 ; k < nodeNum; k ++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nodeNum; i ++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < nodeNum; j ++) { if (connect[i][j] == -1 && connect[i][k] != -1 && connect[k][j] != -1 ) { connect[i][j] = connect[i][k] * connect[k][j]; } } } } for (auto query : queries) { string a = query[0 ], b = query[1 ]; int ia = nodes.find (a) != nodes.end () ? nodes[a] : -1 ; int ib = nodes.find (b) != nodes.end () ? nodes[b] : -1 ; if (ia != -1 && ib != -1 ) { result.push_back (connect[ia][ib]); } else { result.push_back (-1 ); } } return result; }
判断有向图存在环路
leetcode207 课程表
你这个学期必须选修 numCourses 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1 。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 先修课程按数组 prerequisites
给出,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示如果要学习课程 ai 则 必须
先学习课程 bi 。 例如,先修课程对 [0, 1] 表示:想要学习课程 0
,你需要先完成课程 1 。
请你判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回
false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 bool canFinish (int numCourses, vector<vector<int >>& prerequisites) vector<vector<int >> edges (numCourses); vector<int > father (numCourses, 0 ) ; for (int i = 0 , len = prerequisites.size (); i < len; i ++) { int a = prerequisites[i][0 ]; int b = prerequisites[i][1 ]; edges[a].push_back (b); father[b] ++; } queue<int > learn; for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i ++) { if (! father[i]) learn.push (i); } int count = 0 ; while (learn.size ()) { count ++; int node = learn.front (); learn.pop (); for (auto edge : edges[node]) { if (-- father[edge] == 0 ) { learn.push (edge); } } } return count == numCourses; }